Since 2011, the International Development Finance Club (IDFC), a group of 27 national and regional development banks with over USD 4 trillion in combined assets and annual commitments exceeding USD 1.3 trillion, has conducted an annual mapping of member institutions’ green finance contributions.
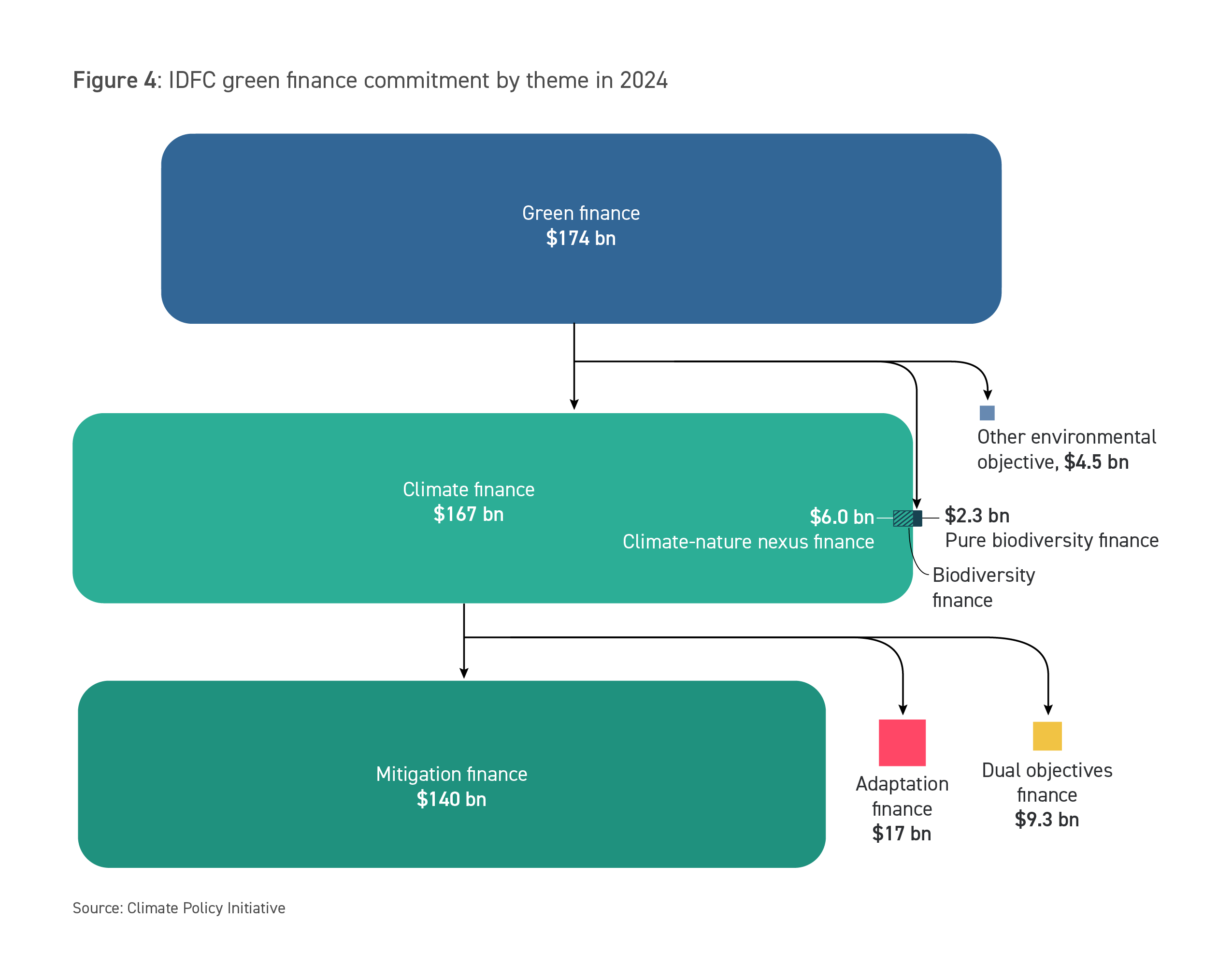
In 2024, IDFC members reported USD 174 billion in total green finance commitments. While the overall level decreased by 13% in 2024—due to changes by a few large reporting institutions—the majority of IDFC members continue to show increased engagement in green finance: 14 of the 23 members responding to survey increased their total green finance commitments. Participation in the IDFC’s Green Finance Mapping survey remained steady in 2024, with 23 institutions responding and 8 of those reporting biodiversity commitments.
Key findings
- IDFC members reported green finance commitments of USD 174 billion in 2024, a 13% decrease from 2023.
-
In 2024, green finance represented 13% of total new commitments reported by IDFC members, compared with shares ranging from 19% to 24% over the preceding four years.
-
Climate finance—all activities related to the mitigation of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, adaptation to climate change or dual objectives—accounted for 96% of total green finance (or USD 167 billion), on par with the share in 2023.
-
Mitigation finance continued to dominate at USD 140 billion, representing 84% of climate finance, a slight decline from USD 175 billion in 2023.
-
Adaptation finance totaled USD 17 billion in 2024, an increase of 64% from 2023. This growth was largely driven by members with larger portfolios, including the China Development Bank (CDB), which doubled its investments since 2023. Meanwhile, the number of survey respondents reporting adaptation finance fell by 20%, and only half of members reporting adaptation finance increased their commitments in 2024.
-
Finance to projects supporting both mitigation and adaptation efforts—“dual-objective finance”—totaled USD 9 billion in 2024, a 15% decrease from 2023. These flows represented 6% of total climate finance, just consistent from 6% in 2023, indicating a proportional decline rather than a structural shift. Dual-benefit finance remains important for supporting adaptation objectives, underscoring the ongoing relevance of integrating both mitigation and adaptation considerations into climate commitments.
-
-
Finance for biodiversity projects rose in 2024 to reach USD 8 billion. This includes finance for dedicated conservation activities as well as for water supply, wastewater treatment, and agriculture and natural resources management projects that deliver biodiversity benefits. While many members do not yet track biodiversity finance, several reported undertaking strategy development or piloting the IDFC biodiversity tool. These efforts are expected to support future increases in both the volume of biodiversity finance reported and the number of members tracking it.
-
Additionally, IDFC members reported USD 4 billion in financing for other environmental objectives, including projects for the circular economy and reducing pollution.